Liver Transplant
- Medical Specialities
- Liver Care
- Liver Transplant
-
Liver Transplant Surgery and Comprehensive Care
-
When the liver stops functioning adequately due to chronic liver disease or injury, a liver transplant becomes the definitive treatment. At Zydus Hospitals, one of the best liver transplant hospitals in Ahmedabad, we provide comprehensive evaluation, advanced surgical care, and post-operative support to ensure long-term recovery and quality of life.
-
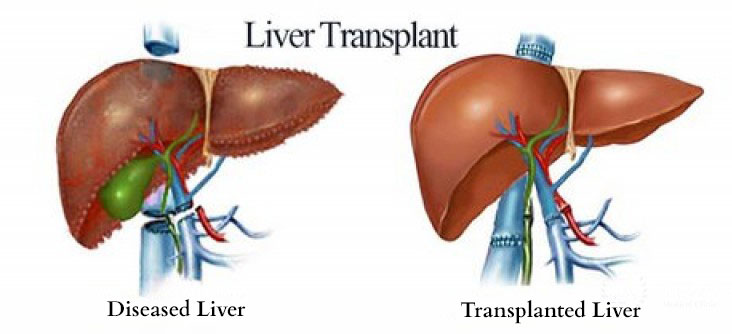
A liver transplant is a complex surgical procedure performed to replace a damaged or diseased liver with a healthy liver from another person, the donor. The transplanted liver may come from a living donor or a deceased donor.
-
Since the liver has natural regenerative capacity, even a portion transplanted from a living donor can grow to normal size within a few weeks. This makes living donor liver transplant (LDLT) a viable and life-saving option.
-
A liver transplant in India is typically advised for patients with end-stage liver disease or acute liver failure, when other treatments no longer work.
-
Common conditions that may require a cirrhosis liver transplant or other forms of transplant include:
-
End-stage cirrhosis (any cause)
-
Acute Liver Failure (ALF)
-
Liver cancer within transplant criteria
-
Severe ACLF with multi-organ failure
-
Alcohol-related liver disease
-
Chronic viral hepatitis (Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C)
-
Autoimmune hepatitis
-
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
-
Genetic and metabolic diseases like Wilson’s disease and Hemochromatosis
-
Bile duct diseases such as primary biliary cholangitis and biliary atresia
-
Vascular disorders (e.g., Budd-Chiari syndrome)
-
Certain types of primary liver cancer, such as hepatocellular carcinoma
-
Indications in Children include:
-
Biliary atresia
-
Acute liver failure
-
Metabolic liver disease
-
Congenital liver disorders
What Is a Liver Transplant?
Who Needs a Liver Transplant?
-
Before a transplant, the transplant team evaluates the liver transplant criteria carefully to ensure patient safety and the best outcomes.
-
Evaluation includes:
-
Identifying the cause and stage of liver failure
-
The MELD score for liver transplant (Model for End-Stage Liver Disease) is used to assess the urgency for transplant. Higher scores indicate more severe disease.
-
Detailed blood and imaging investigations, including liver and kidney function tests, CT scans, MR venography, and Doppler ultrasounds
-
Assessment of heart, lung, and overall health fitness
Liver Transplant Criteria
-
Depending on the source of the donor and surgical technique, there are several types of liver transplant:
Types of Liver Transplant
1. Living Donor Liver Transplant (LDLT)
In this liver transplant procedure, a part of the liver (usually the right or left lobe) is taken from a living donor, often a relative with a compatible blood group. The donor’s liver regenerates to near-normal size within 6-8 weeks.
2. Cadaveric (Deceased Donor) Liver Transplant
Also known as a cadaveric liver transplant or deceased donor liver transplant (DDLT), this procedure uses a liver from a brain-dead donor whose family has consented to organ donation. Allocation depends on blood group matching and MELD score priority.
-
Living Donor Criteria
-
Aged 18-55 years
-
A close relative (1st or 2nd degree) or voluntary donor
-
Blood group compatible with the recipient
-
Physically and mentally healthy, with no major co-morbidities
-
Donor evaluation includes blood tests, liver volumetric scans, and psychological assessment
-
Donation is completely voluntary and non-commercial
Liver Transplant Donor and Donor Criteria
A liver transplant donor may be a living or deceased individual. To ensure donor and recipient safety, specific liver transplant donor criteria are followed:
The liver regenerates fully in about 6-8 weeks, and the donor typically resumes normal life soon after recovery.
-
1. Liver ICU Care
-
Continuous hemodynamic monitoring
-
Ventilation management
-
CRRT (if required)
-
Antibiotic stewardship
-
Graft function monitoring
-
Immunosuppression initiation
-
2. Infection Prevention
-
Strict sterile protocols
-
Early detection of sepsis
-
Tailored prophylaxis
-
3. Rejection Monitoring
-
LFT trends
-
Doppler ultrasound
-
Biopsy in selective cases
-
4. Long-Term Follow-Up
-
Regular clinic visits
-
Medication optimization
-
Nutrition guidance
-
Lifestyle counselling
Post-Transplant Care at Zydus
-
Highly specialized pediatric hepatologists
-
Pediatric anesthesia experts
-
Pediatric critical care specialists
-
Experienced transplant surgeons
Pediatric Liver Transplant
Pediatric liver transplant is indicated for children with end-stage liver disease, acute liver failure, or certain genetic and metabolic disorders affecting liver function.
The procedure restores normal liver function, allowing children to grow, develop, and lead healthier lives.
As children have unique physiology, liver growth patterns, and metabolic needs, managing liver disease in children requires:
Zydus Hospitals provides all these under one roof.
-
Patients are guided on diet, hygiene, and medication adherence.
-
Masks and crowd avoidance are recommended for about 3 months.
-
Regular blood tests ensure proper liver function and early detection of rejection.
-
Most patients return to normal activities or work within 3 months.
-
ICU monitoring for graft function
-
infection prevention
-
Immunosuppressive therapy
-
Growth & development monitoring
-
Vaccination planning
Liver Transplant Recovery
After the liver transplant surgery, patients are monitored closely in the ICU for 5-7 days. Hospital stay generally lasts 2-3 weeks for observation, physiotherapy, and immunosuppressant adjustments.
During recovery:
Post-Transplant Care for Children includes:
Zydus ensures long-term follow-up through its Pediatric Liver Clinic and experienced pediatric hepatologists.
Life After Liver Transplant
Life after a liver transplant in Ahmedabad at Zydus Hospitals can be healthy and productive. With proper medication, lifestyle care, and follow-up, patients can expect a long-term normal life expectancy.
For donors, the liver regenerates completely within 1.5-2 months. No lifelong medication is required, only periodic check-ups for a year. Both recipients and donors are advised to avoid smoking and alcohol permanently.
Zydus Hospitals Leading Centre for Liver Transplant in India
With advanced transplant infrastructure, a dedicated team of hepatologists, anesthesiologists, and surgeons, Zydus Hospitals is recognized as one of the best liver transplant hospitals in Ahmedabad. Our experts have successfully performed complex procedures, including ABO-incompatible and orthotopic liver transplants, following globally accepted protocols for safety and recovery.

Search Doctor / Diseases