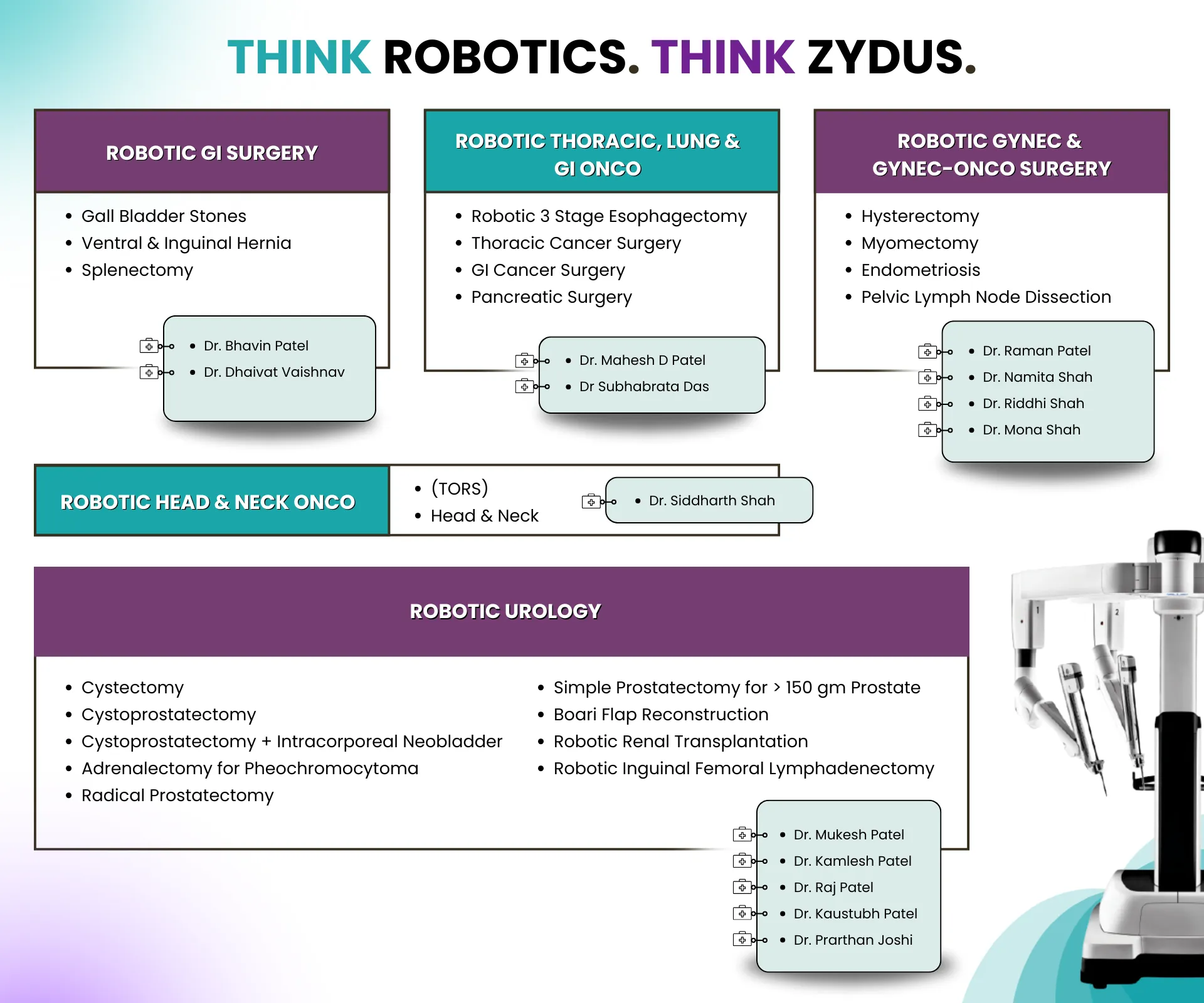
Allergy Treatments And Immune System Disorders Treatments
- Medical Specialities
- Allergy, Immunology & Rheumatology
Immunology is a branch of biomedical science that studies the body's immune system, which serves as a defence mechanism against infections and other harmful invaders. The immune system identifies and responds to antigens—substances perceived as foreign or dangerous. Additionally, immunology addresses immune system dysfunctions, such as allergies, hypersensitivities, immune deficiencies, transplant rejection, and autoimmune disorders. Clinical immunologists specialize in diagnosing and managing these conditions.
Mechanisms of Immune System Disorders
-
Immunodeficiencies Immunodeficiency disorders compromise the body's ability to fight infections, rendering individuals susceptible to bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections. These disorders may be classified as either:
-
Primary immunodeficiencies (congenital): Result from genetic defects and are present from birth. They may involve deficiencies in components such as B cells, which produce antibodies, or T cells, which regulate immune responses.
-
Secondary immunodeficiencies (acquired): Develop later in life due to external factors, including infections (e.g., HIV/AIDS), medical treatments (e.g., chemotherapy, radiation), malnutrition, or chronic illnesses (e.g., diabetes, cancer). Aging can also contribute to immune system decline.
-
-
Allergies- Also known as hypersensitivities, occur when the immune system overreacts to harmless environmental substances known as allergens. The process involves:
-
Sensitization: Initial exposure to an allergen triggers the production of Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies specific to that allergen.
-
Mast Cell Activation: IgE antibodies attach to mast cells, and upon subsequent allergen exposure, the allergen binds to these antibodies, prompting mast cells to release histamine and other inflammatory mediators.
-
Allergic Reactions: This immune response can affect the skin, airways, mucous membranes, and digestive tract, leading to symptoms such as itching, swelling, respiratory distress, or gastrointestinal discomfort.
-
-
Rheumatic Diseases- Also termed as musculoskeletal diseases, encompass a broad spectrum of conditions affecting joints, muscles, bones, and connective tissues. Many of these disorders are autoimmune in nature, wherein the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, leading to inflammation, pain, and potential tissue damage. Some key characteristics include:
-
Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: Examples include rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, where immune dysregulation results in chronic inflammation.
-
Degenerative Rheumatic Diseases: Conditions such as osteoarthritis arise from wear and tear on joints rather than immune dysfunction
-
Causes and Risk Factors: Genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and, in some cases, prior injuries that failed to heal properly may contribute to the onset of these disorders.
-
-
The immune system plays a crucial role in protecting the body against harmful invaders, but its dysfunction can lead to various disorders, including immunodeficiencies, allergies, and rheumatic diseases. Understanding the mechanisms underlying these conditions is essential for their diagnosis, treatment, and management. Clinical immunologists and rheumatologists play a vital role in advancing therapies to improve patient outcomes.
When to Consult an Immunologist, Allergist, or Rheumatologist
A. When to See an Immunologist (Allergist)?
One should consider consulting an immunologist, who may also specialize in allergies (allergist), if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent allergies lasting several months each year.
- Allergy symptoms leading to complications such as chronic sinus infections or difficulty breathing.
- Signs of asthma, including frequent wheezing, coughing (especially after exercise), occasional shortness of breath, or chest tightness.
- Frequent asthma attacks despite using prescribed medications.
- Severe allergic reactions, including hives, facial or tongue swelling, or breathing difficulties.
- Allergies that are not effectively managed with over-the-counter medications or lifestyle modifications.
- Allergies or asthma affecting your quality of life, work, or recreational activities.
- Frequent infections or prolonged recovery from common illnesses, which may indicate an underlying immunodeficiency.
- A known family history of immunodeficiency disorders.
- Symptoms suggestive of autoimmune diseases, such as frequent fevers, fatigue, joint pain or swelling, or unexplained skin issues.
B. When to See a Rheumatologist-
One should seek an appointment with a rheumatologist if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent allergies lasting several months each year.
- Allergy symptoms leading to complications such as chronic sinus infections or difficulty breathing.
- Signs of asthma, including frequent wheezing, coughing (especially after exercise), occasional shortness of breath, or chest tightness.
- Frequent asthma attacks despite using prescribed medications.
- Severe allergic reactions, including hives, facial or tongue swelling, or breathing difficulties.
- Allergies that are not effectively managed with over-the-counter medications or lifestyle modifications.
- Allergies or asthma affecting your quality of life, work, or recreational activities.
- Frequent infections or prolonged recovery from common illnesses, which may indicate an underlying immunodeficiency.
- A known family history of immunodeficiency disorders.
- Symptoms suggestive of autoimmune diseases, such as frequent fevers, fatigue, joint pain or swelling, or unexplained skin issues.
For further details or to schedule an appointment, please contact Zydus Hospitals Ahmedabad through the official contact information available on their website.