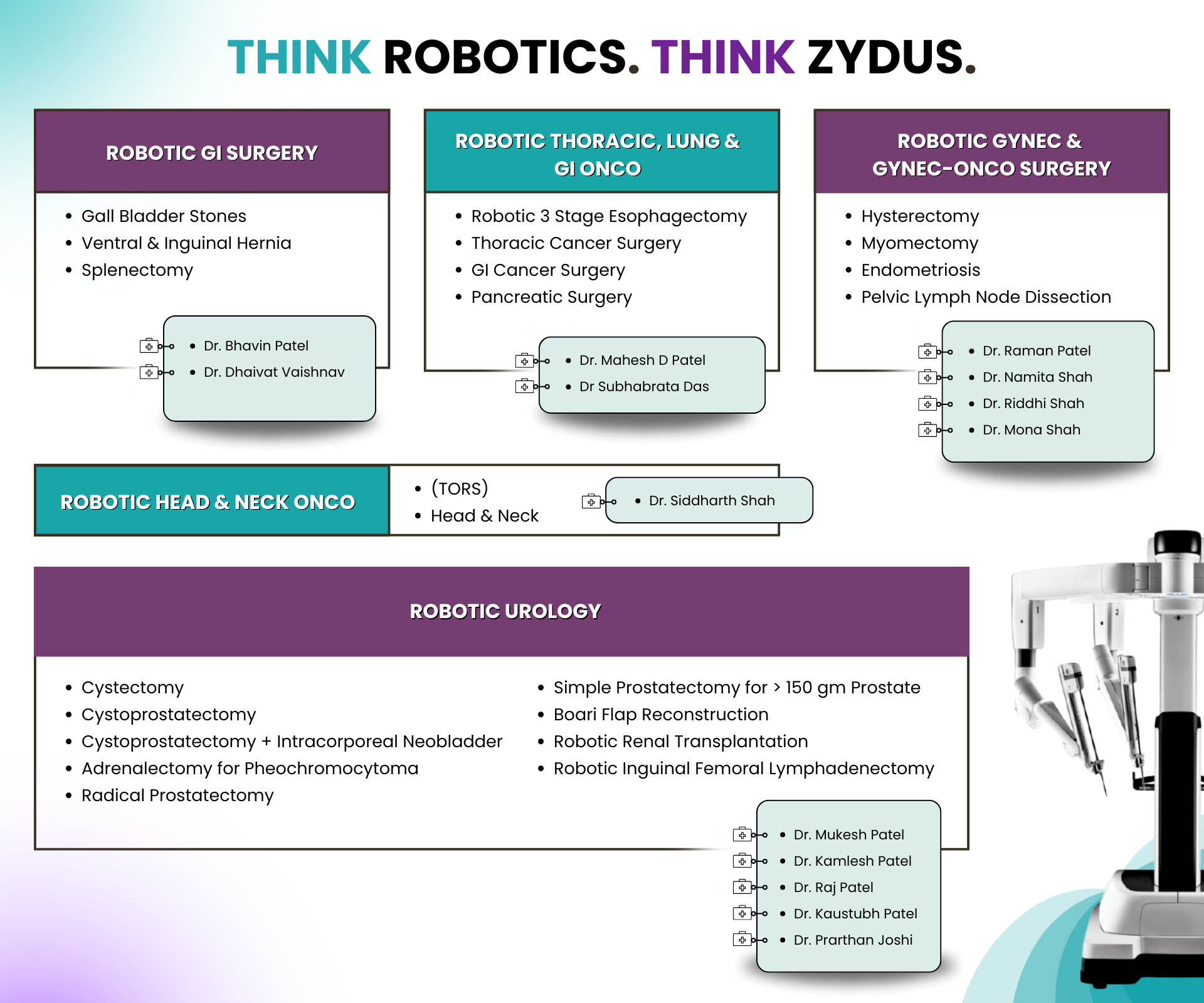
ALD and NAFLD Treatment
- Medical Specialities
- Liver Care
- ALD and NAFLD
-
ALD and NAFLD
-
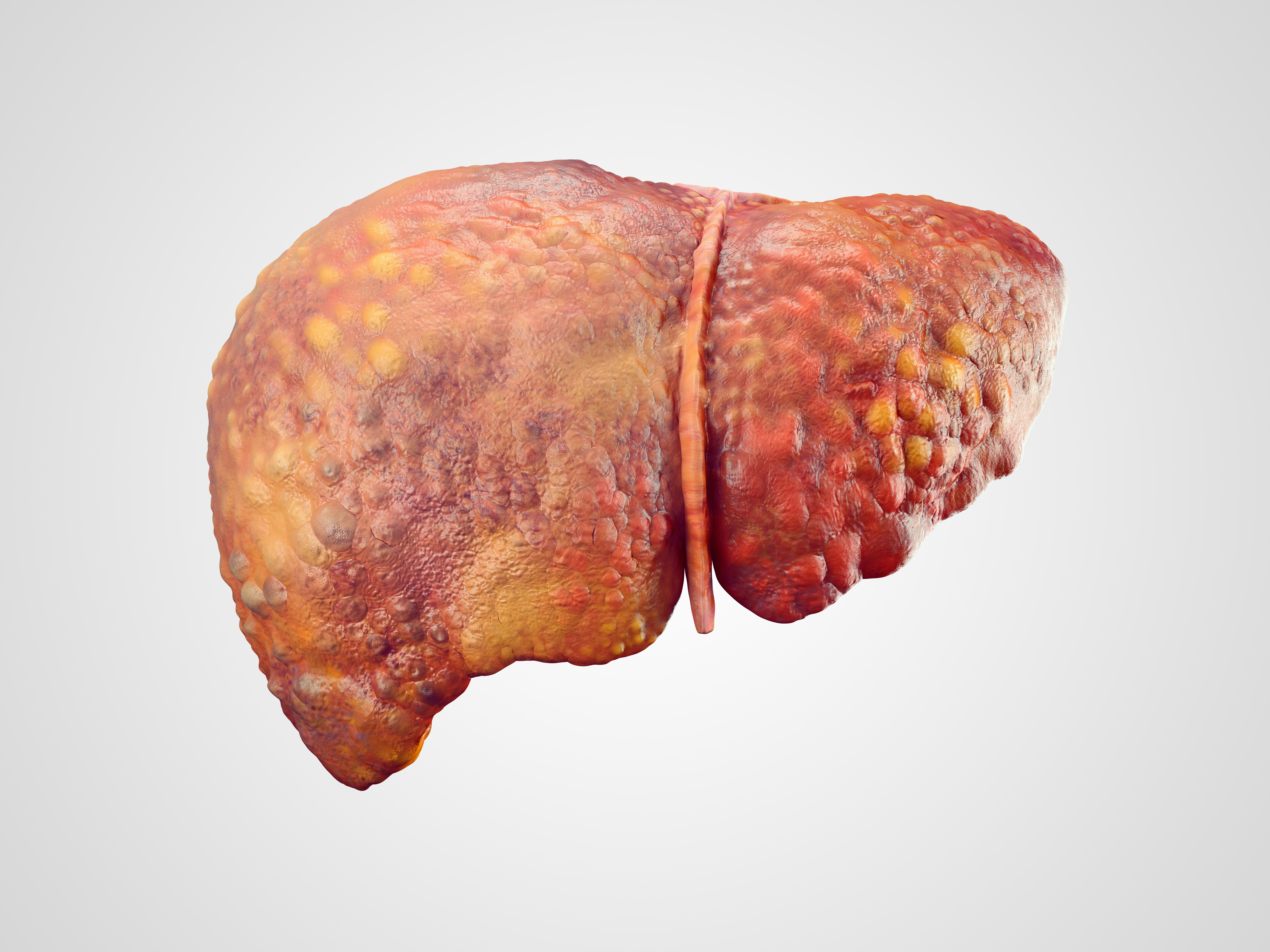
Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD) is caused by excessive alcohol consumption, where fat is accumulated over the liver and leads to liver damage. The common symptoms are fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice, weight loss, and loss of appetite.
-
The common prevention is to limit alcohol consumption.
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
-
It is a condition in which fat accumulates in the liver, and is unrelated to alcohol consumption. It’s usually associated with obesity and diabetes. The common symptoms are fatigue, abdominal pain, jaundice, itchy skin, and swelling in the legs/ankles/ abdomen.
-
NAFLD can be prevented by consuming a healthy diet, exercising regularly & proper weight management.
-
The Prevention for NALFD Healthy diet is exercise & weight management.
-
Liver Tests
-
Liver Tests (LTS), often called Liver Function Tests, are blood tests that monitor the health of the Liver and the Bile ducts. Along with one’s history and physical examination, the Liver Tests guide the healthcare provider to diagnose and manage Liver disease, if any.These tests measure the levels of certain enzymes and proteins in the blood, how well the liver is performing its functions, and measure enzymes that liver cells release in response to damage or diseases.
- Serum Bilirubin test (direct and indirect) to ascertain jaundice and its type
- Enzymes Alanine Aminotransferase - ALT (previously called SGPT)
- Aspartate Aminotransferase - AST (previously called SGOT)
- Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
- Gamma Glutamyl Transferase (GGT)
- Proteins and Albumin test
- Prothrombin time and INR (PT/INR)
- Hepatitis A - HEP A IgM
- Hepatitis B - HBsAg / ABV / DNA / PCR
- Hepatitis C - HCV / RNA
- Cytomegalo Virus (CMV) - CMV IgG, CMV IgM
- Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) - IgG, IgM
- HIV
- Antinuclear Antibody Test (ANA)
- Liver Kidney Microsomal Antibody (LKMA)
- Anti-Smooth Muscle Antibodies (ASMA)
- Alpha-Fetoprotein (AFP)
- Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA)
- Prothrombin Induced by Vitamin K Absence (PIVKA)
- PET CT SCAN
- Diabetes panel (Fasting, PPBS, HbA1c, Lipid profile)
- It is a diagnostic procedure used to obtain a small amount of liver tissue, which is then examined under a microscope to determine what is causing the liver disease, as well as the degree of fibrosis (scarring) of the liver.
- Detailed evaluation should be always done by a liver specialist. These tests are used to evaluate the function of the liver and to diagnose various liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, fatty liver disease, and liver cancer. Some tests, such as the bilirubin test and liver enzymes, can help determine the cause and severity of jaundice, while others, such as the prothrombin time and INR, assess the liver's ability to produce clotting factors. A liver biopsy and endoscopic examination are invasive procedures that can provide detailed information about the liver's structure and function and are often used to diagnose liver disease and monitor treatment response.
A fibroscan probe sends sound waves that bounce back at different speeds depending on liver stiffness. Thus measuring the stiffness quantitatively.
- Non Invasive & Painless
- Precise results in short time
- Vibration Controlled Transient Elastography (VCTE) technology
- Assesses liver fibrosis or scarring caused by various liver conditions
- Can perform diagnosis without Biopsy
- Produces biomarkers that can assess and monitor patients over time
- Uses uniform algorithms that minimize inter-operator variability eliminating inter-system variability
- Measures liver stiffness, an indicator for fibrosis
-
Liver Transplant
-
When the liver doesn’t function adequately or liver disease has progressed onto higher stages and it is damaged beyond repair, liver transplant is recommended.
-
It is a surgical procedure performed to remove part of a diseased or injured liver and replace it with a whole or a portion of a healthy liver from another person (dead or alive), called the donor. Since the liver has regenerative properties, a transplanted segment can grow to normal size within a matter of few weeks.
-
The new Liver can be from two sources:
-
Living Donors: from one’s own family, or someone who is blood group compatible. It is called Living Donor Liver Transplant (LDLT).
-
Deceased Donors: from a brain-dead person whose family has agreed for donation. It is called Deceased Donor Liver Transplant (DDLT).

-
The transplanted Liver then continues to function in the new body – the host body – under cover of immuno-suppressants
-
A related living donor with a matching blood group can donate up to 70% portion of their liver
-
This process ensures that those in need of a liver transplant have options based on their condition and available donors
-
Recently the experts at Zydus hospital have also performed ABO incompatible Liver Transplant.
-
The causes for Liver Transplant are
-
- Alcohol related Liver diseases
- Chronic Hepatitis, including hepatitis B and Hepatitis C.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis Disease caused by abnormality of the immune system
- Vessel Diseases - Budd Chiari Syndrome
- NASH, or Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis, a disease caused by buildup of fat in the liver
- Some genetic conditions, including Wilson disease, where dangerous levels of copper build up in the liver, and Hemochromatosis where iron builds up in the liver
- Bile duct Diseases - Primary biliary cholangitis, Primary sclerosing cholangitis, and biliary atresia
- Primary liver cancer that originate in the liver, such as hepatocellular carcinoma,is amenable to liver transplant. Unfortunately, in most cases, individuals are diagnosed late, making transplant impossible.
-
Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation
-
- Organs come from brain-dead donors
- Allocation is done based on blood group and MELD score
- MELD score (6-40) indicates the patient's condition
- A higher MELD score gets priority for a matching liver
-
Living Donor Transplantation
-
- Donor needs to be from the family (1st or 2nd - degree relative).
- Donor should be a healthy individual or with controlled co-morbidities.
- Donor's blood group has to be matched or compatible.
- Age of donor should be between 18-55 and in a sound state of mind.
- The donation must be voluntary and not under coercion or financial incentives.
-
The donor is selected and evaluated on the basis of the following:
-
Evaluation of Recipient
-
- Finding out the etiology of acute liver failure / chronic liver disease
- Haematological and Biochemical evaluation: Complete blood count, Liver and renal function tests.
- Lipid profile, Iron studies, Cytomegalovirus IgG/IgM
- Thyroid profile
- 24-hour urine analysis
- Tumour markers
- Cultures (blood and urine c/s)
- Imaging studies
- Ultrasound of the abdomen with Doppler studies
- Triphasic CT scan of the abdomen
- Bone scan and high-resolution CT scan of the chest
- MRI with Venography
- Patient is under general anaesthesia
- Damaged liver is removed
- Donor liver is implanted and connected to blood vessels and bile ducts
- Recovery
- Expect pain and discomfort
- Hospital stay for 2-3 weeks for monitoring, immunosuppressant dose adjustment, and rehabilitation
- Medications to prevent rejection and manage issues
- Regular check-ups with transplant team for liver function and health
- Discharged within 2-3 weeks
- Wear masks, avoid crowds for 3 months
- Regular blood reports with follow-up
- Quality of life returns to normal and patient can resume work in 3 months
- Liver regenerates within 1.5-2 months
- Regular follow-ups with tests for one year
- No lifelong medication
- No restrictions, except no smoking or alcohol consumption
-
Liver Cancer
-
Liver cancer is related to its drainage system or rising from gall bladder and bile duct. It’s complex disease and the common causes are Hepatitis B and C virus, Cirrhosis, alcohol related cirrhosis, fatty liver. It is curable in medical science. There are four types with which this can be treated:
-
- Embolization Therapy
- Transarterial Embolization (TAE)
- Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE)
- Ablation Therapy
- Surgery
- Liver Transplant
- Radiation Therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted Therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Embolization Therapy

FAQ
-
Yes, both the recipient and donor need to undergo various tests before the transplant. These are necessary to determine the fitness and eligibility of the donor to donate and the recipient to receive the liver.
-
The transplant operation estimate includes - hospital stay for the recipient (up to 21 days) and donor (up to 7 days); both the donor & recipient surgeries; all visits by the transplant team (surgeons and hepatologist), Doppler ultrasound for the first 5 days for the recipient and 1 day for the donor; medical consumables and medicines used during and after the operation.
-
Basic reports of the patient need to be e-mailed, based on which we can issue a letter to facilitate visas for the donor and attendants. Normally up to two attendants are allowed to come apart from the donor and the recipient.
-
There is a legal committee that will go through the documentation of the donor's relationship with the recipient. The hospital’s coordinator will help the patient to collate these papers. Donor and recipient will need to provide the original documents as needed.
-
Recipient test: Blood group, LFT (Liver Function Test), RFT (Renal Function Test), IN (International Normalized Ratio), CBC (Complete Blood Count), CT scan triphasic of liver, HBsAg, Anti HCV.
Donor test: Blood group, CBC, LFT, RFT, HBsAg, Anti HCV, LAI (Liver Attenuation Index) - CT scan of liver.

Search Doctor / Diseases
The Transplant Center of Gujarat
-
LIVER TRANSPLANT
-
200+ successful transplants done
-
A full-time dedicated team of 20+ members of Liver Transplant Surgeons, Hepatologists, Intensivists and Anaesthetists
-
Exclusive Class 100 Modular Liver OT and Liver ICU with strong infection control standards
-
KIDNEY TRANSPLANT
-
300+ successful transplants completed by the experienced and dedicated team of Senior Consultants in Nephrology and Urology
-
State-of-the-art 50 bed advanced Dialysis Centre with facilities for CRRT, SLED, HDF and CytoSorb
-
HEART TRANSPLANT
-
Highly experienced team of Heart Transplant Surgeons and Cardiologists
-
State-of-the-art infrastructure with exclusive Cardiac Critical Care Unit, ECMO Facility, Advanced Cath Lab and Left Ventricular Assist Device (artificial heart) Facility
-
BONE MARROW TRANSPLANT
-
200+ Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplants at hi-tech BMT Unit
-
Highly experienced Haematologist, Intensivists and BMT-trained Staff, supported by Radiation Oncology Department with TBI treatment