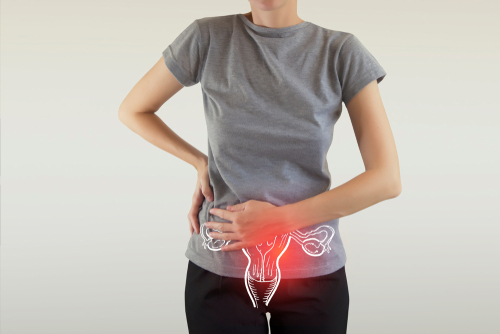
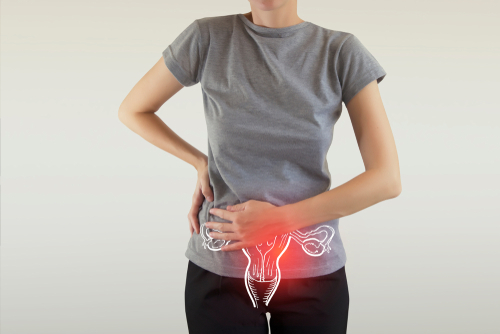
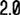Symptoms of Peritonaeal Cancer:
- Abdominal discomfort or pain from gas, indigestion, pressure, swelling, bloating, or cramps
- Feeling of fullness, even after a light meal
- Nausea or diarrhoea
- Constipation
- Frequent urination
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight gain or loss
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Rectal bleeding
- Shortness of breath
Treatment of Peritoneal Cancer
HIPEC
HIPEC stands for Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy. The aim of a HIPEC operation is to remove as much of the cancer as possible and then destroy any cancers cells that can’t be seen with the naked eye by putting hot chemotherapy inside the abdomen.
PIPAC
PIPAC stands for Pressurised Intra Peritoneal Aerosolised Chemotherapy. PIPAC is part of a clinical trial to see if it can shrink secondary cancers growing on the inside lining of the abdominal cavity (known as the peritoneum). These tumours are known as peritoneal metastases.
PIPAC is a type of chemotherapy given directly into a patient’s abdomen during an operation. After PIPAC is given, it stays inside the abdomen for 30 minutes, with the whole operation takes approximately two hours.
How PIPAC and HIPEC is Different?
Not all patients can undergo a HIPEC operation. One of the main reasons for this is some patients have too many tumours in their peritoneum. This is where PIPAC comes into play. The aim of the PIPAC operation is to get control of the cancer by shrinking the number and size of the tumours in the peritoneum. For some patients these tumours may shrink enough to mean that a HIPEC operation becomes possible in the future.