ENT Surgery (Ear, Nose & Throat Surgery)
Medical Specialities / ENT Surgery
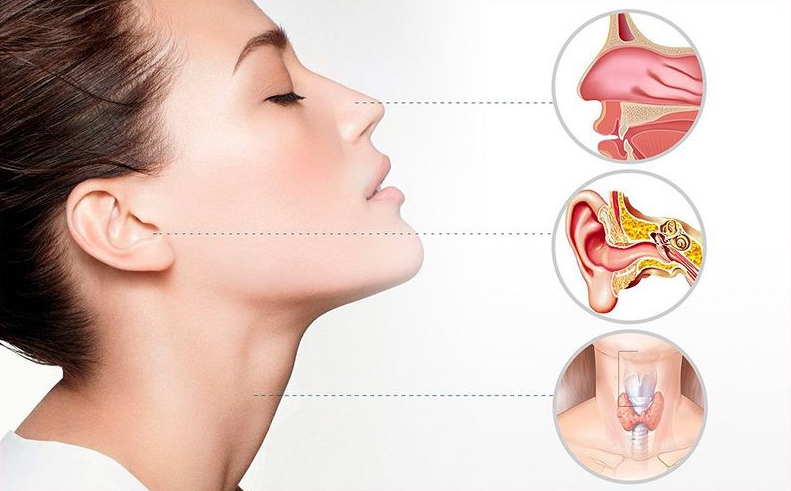
Otology is a branch of biomedicine which studies normal and pathological anatomy and physiology of the ear (hearing and vestibular sensory systems and related structures and functions) as well as its diseases, diagnosis and treatment.
Rhinology is the study of the nose, including the sinuses. Rhinology concerns itself with medical and surgical diseases of the nasal passages as well as paranasal sinuses. It is becoming more important after the introduction of nasal endoscopes. A rhinologist is a specialist otolaryngologist who specifically treats the nose.
When blood flow and oxygen supply to the heart are reduced or cut off, you can develop:
Laryngology is that branch of medicine which deals with the illnesses and injuries of the larynx. Common pathologies addressed by laryngologists include vocal cord polyps, cysts, nodules, and cancer.
Patients first involved adapting operating techniques and robot-arm positions, and continually refining those adaptations, Carroll said. The da Vinci was originally designed for operating on the lower and middle sections of the body, not the narrow spaces inside the head and neck. The increased surgical accuracy comes from tiny cameras attached to the end of the da Vinci instruments. Carroll said the magnified, 3-D image gives doctors a greater field of vision than conventional open or laparoscopic surgery.
Facial plastic surgery treats a specific component of these conditions and can be divided into two types - reconstructive and cosmetic. Reconstructive plastic surgery is performed for patients with conditions that may be present from birth, such as birthmarks on the face, cleft lip and palate, protruding ears, and a crooked smile. Other conditions that are the result of accidents, trauma, burns, or previous surgery are also corrected with this type of surgery. In addition, some reconstructive procedures are required to treat existing diseases like skin cancer. Cosmetic facial plastic surgery is surgery performed to enhance visual appearance of the facial structures. Typical procedures include facelifts, eye lifts, rhinoplasty, and liposuction. An otolaryngologist surgeon is well trained to address all of these problems.
Laser surgery is useful in the treatment of ear, nose, and throat diseases in children, especially allergic rhinitis, recurrent laryngeal papillomatosis, infantile subglottic hemangioma. Hypertrophied nasal mucosa caused by allergic rhinitis was vaporized using KTP laser safely with little bleeding. KTP laser is powerful in treatment of recurrent laryngeal papillomatosis and subglottic hemangioma. However, we have to mind the complications of laryngeal stenosis by using laser technique.
Sleep apnea treatment varies depending on the individual. Some people find relief from sleep apnea and snoring through surgery. Others control their sleep apnea with a CPAP machine or other mechanical means. Sleep apnea treatment also includes oral applications that use dental mouthpieces, and simple lifestyle changes. Bear in mind there is no cure for sleep apnea: treatment focuses on keeping the airways open and promoting a good night's sleep.
Micro ear surgery is done with a surgical microscope. Surgery for the human sensory organs like the ear requires precision to achieve desirable results. The unaided eye is not adequate to visualize and work in the narrow confines of the ear where dimensions are measured in millimeters. Holmgren was the first among the many surgeons who pioneered the development of the microsurgery for the ear using surgical microscopes. He used magnification spectacle loupes with the surgical microscope to perform fenestration operations in the 1930's for the disease of otosclerosis. The American Surgeon Shanbaug in 1940 converted a dissection surgical microscope by adding a light source for illumination in the surgical microscope thus opening a new vista in reconstructive ear surgery.
Endoscopic sinus surgery - also called endoscopy or sinoscopy - is a procedure used to remove blockages in the sinuses (the spaces filled with air in some of the bones of the skull). These blockages cause sinusitis, a condition in which the sinuses swell and become clogged, causing pain and impaired breathing. A thin, lighted instrument called an endoscope is inserted into the nose, and the doctor looks inside through an eyepiece. Much like a telescope with a wide-angle camera lens, the endoscope beams light into different parts of the nose and sinuses, allowing the doctor to see what is causing blockages. Surgical instruments can then be used along with the endoscope to remove the blockages and improve breathing.
Laryngoscope can be used for office-based diagnostics. The patient remains wide awake during the procedure, so the vocal fold can be observed during speech or singing. Surgical instruments passed through the scope can be used for performing procedures such as biopsies of suspicious masses.
Adults and children with obstructive sleep apnea have a smaller airway compared to individuals without obstructive sleep apnea. Since the hallmark of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome is upper airway obstruction during sleep, surgical management of the condition usually involves enlarging the airway by removal of soft tissues, or by expansion of the jaw structures that are restricting it. Additionally, the laxity of the upper airway can be reduced by surgery, which lessens the obstruction. Since the airway structures of adults and children vary, different surgical concepts and procedures have been developed to accommodate the anatomical differences.
Plastic surgery is structural cosmetic surgery including changing the shape of the nose, ears, chin, cheekbones and neckline, and rejuvenative facial plastic surgery which includes procedures that will reverse the signs of aging.
Cochlear implants are devices inserted under the skull that directly translate sound into electrical impulses in the auditory nerves, and can help people hear when conventional hearing aids are no help.
Synonyms: Brain stem evoked response audiometry, Auditory brain stem response, ABR audiometry, BAER (Brainstem auditory evoked response audiometry). Brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER) is a test to measure the brain wave activity that occurs in response to clicks or certain tones.
Patients with Chakkar or Giddiness/ dizziness are evaluated in the vertigo clinic. Oto Video Endoscopy is available to visualize the Eardrum to assess the Otological causes of Vertigo. Postural Vertigo is Diagnosed using Dix Hallpike testing and Treated in the Clinic itself using special Epleys Exercises. Vertigo Exercises also available in easy to follow picture format very useful for Elderly Patients suffering from Vertigo.
'The Headache Clinic' is a well-established concept for the care of patients who suffer from chronic recurrent headaches. Eyestrain, refractive errors, sinusitis and psychological tension are NOT the most common causes of headache. Many chronic headaches that are wrongly diagnosed so, often turn out to be migraine.
Audiometry is the technique to identify and quantitatively determine the degree of hearing loss of a person by measuring his hearing sensitivity, so that suitable medical treatment or one of the appropriate hearing aids and assistive devices can be prescribed. In audiological investigations, the hearing sensitivity is tested for pure tones, speech or other sound stimuli. The result, when plotted graphically, is called an audiogram. The electronic instrument used for measuring the hearing threshold level is called an audiometer. Using it, the test tones of different frequencies and levels are generated and presented to the patient and hearing thresholds are determined on the basis of patient's response. The auditory system and its disorders are described. Different audiometric tests, techniques and various audiometers are discussed.
Tympanometry testing is used to assess the condition of the ear drum and middle ear. It is performed by inserting a tympanometer into the ear canal. Prior to tympanometry testing, the physician will visualize the ear canal to evaluate for obstruction such as from impacted earwax. The tympanometer looks like an otoscope. However, it delivers soundwaves, while a vacuum creates both positive and negative pressures within the ear canal. The returned energy creates a waveform that a physician can use to evaluate for disorders of the middle ear. This wave form is called a tympanogram.
- Hearing aids makes the sound loud and amplified while cochlear implantation surgery will not only amplify the sound but also make it clearer.
- There is a sound processor device and the microphones on them pick up sounds and the processor converts them into digital information.
- This information is transferred through the coil to the implant just under the skin.
- The implant sends electrical signals down the electrode into the cochlea.
- The hearing nerve fibres in the cochlea pick up the signals and send them to the brain , giving the sensation of sound.